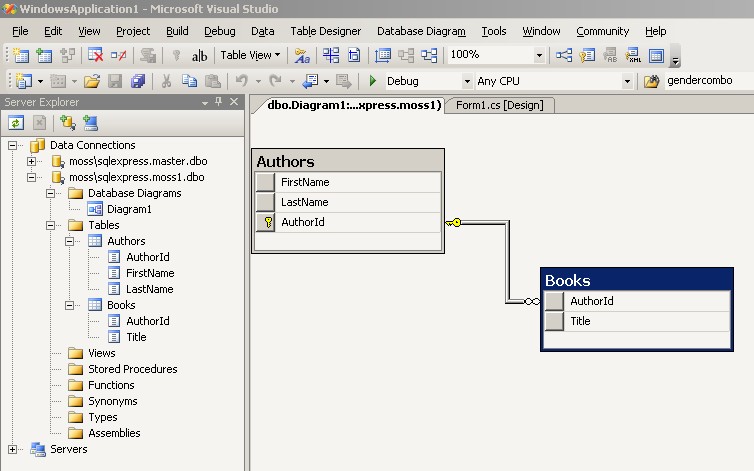
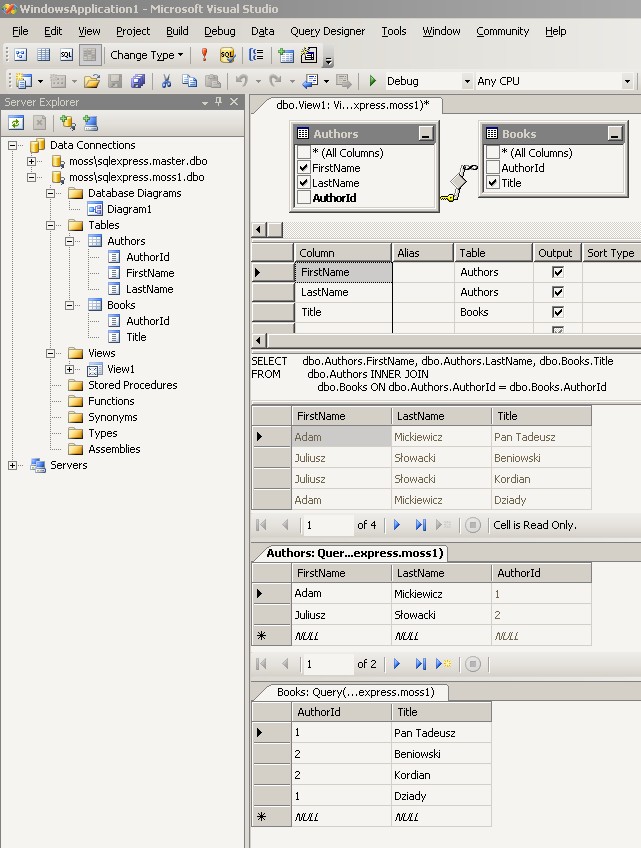
- Using Visual Studio's Server Explorer
- Open the Server Explorer window (menu: View / Server Explorer).
- Add a connection to the SQL Server 2005 Express
(right click on 'Data Connections' node, choose 'Add Connection' and pick
'Microsoft SQL Server' option):
- the name: <machine_name>\SQLEXPRESS,
- the authentication: Windows Authentication,
- click 'Test Connection' button to check the connection.
- SQL Server 2005 Express is a free version of Microsoft SQL Server. It can be used
also in commercial applications. The main drawback of this version is a lack of
administrative tools in its installation (free
Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio Express
must be downloaded separately). Visual Studio can help you to manage your data visually.
- Create a database (click using right mouse button on 'Data Connections' node and choose
'Create New SQL Server Database').
- Your are able to add tables, relations, diagrams, views, stored procedures, triggers, etc. now.
- You can also add data to your tables and execute views and queries.
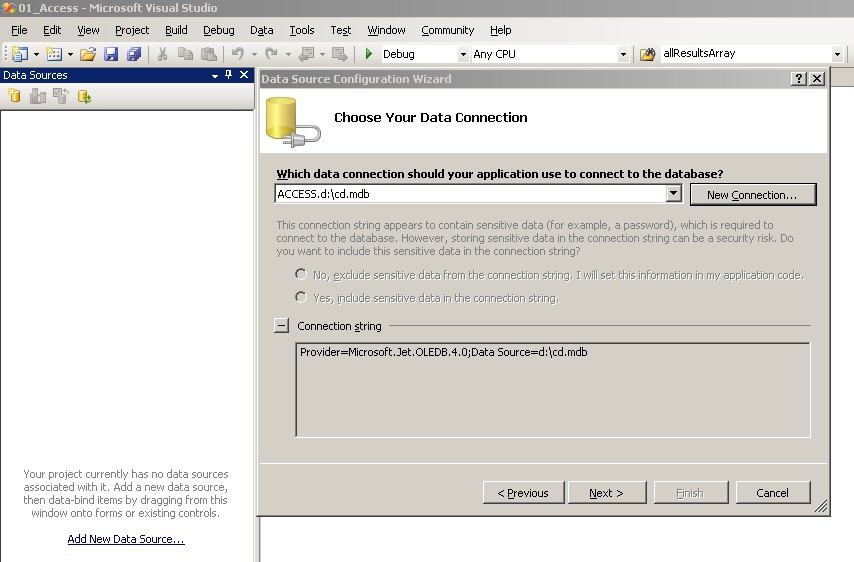
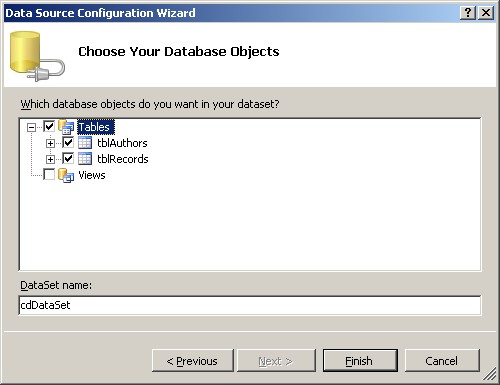
- Using ADO.NET in connected scenario (using DataSets) with an existing Access database.
- Copy and unpack cd.zip file to your local disk.
- Access databases (.mdb files) can be quite efficient solutions: they are binary,
they use indexes and can be used by ADO.NET when Access is not installed.
- Investigate this file using MS Access.
- Access is a quite comfortable solution for small databases. It allows to create
relational databases, design user interface (forms), prepare queries (using SQL),
design reports and web pages. Visual Basic for Applications can be used to create
non-standard solutions.
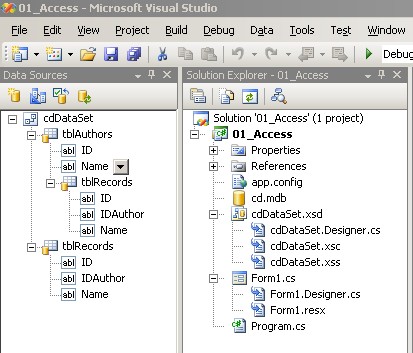
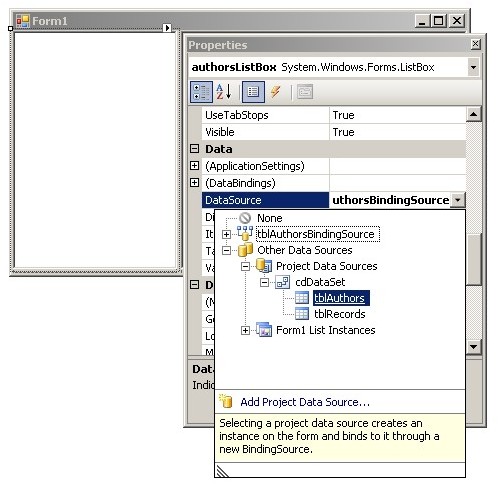
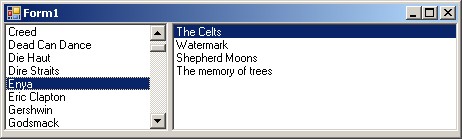
- Create Windows Forms application which will allow to view and edit the database
(name of authors and their records).
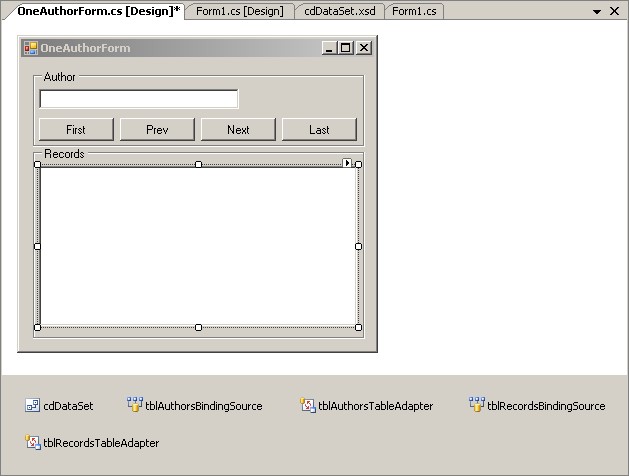
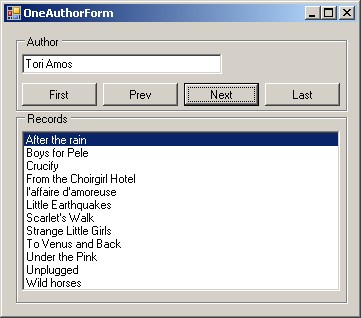
- Create a new Form which will allow to edit names of authors and change
currently selected author using 'Next', 'Prev', 'First', and 'Last'
buttons.
private void FirstButton_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
tblAuthorsBindingSource.MoveFirst();
}
private void PrevButton_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
tblAuthorsBindingSource.MovePrevious();
}
private void NextButton_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
tblAuthorsBindingSource.MoveNext();
}
private void LastButton_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
tblAuthorsBindingSource.MoveLast();
}
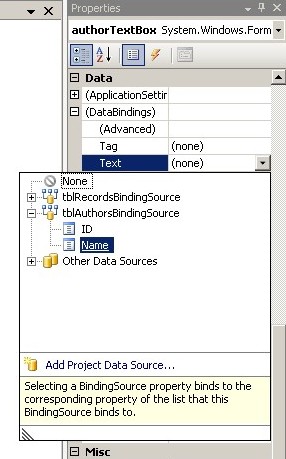
- Implement handler for PositionChange event:
void tblAuthorsBindingSource_PositionChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
tblRecordsBindingSource.Filter = "IDAuthor=" + ((DataRowView)tblAuthorsBindingSource.Current)["ID"];
}
Allow to save changed names of authors
- Add the following code as a handler for FormClosing event.
- Be aware of possibility of replacing the database file
(cd.mdb) in an output directory with the one existing
in a source directory (it depends on the option chosen
during adding connection to the file to a project).
In such case, changes will be saved but replaced again
with original data during the next running the project
from Visual Studio.
private void OneAuthorForm_FormClosing(object sender, FormClosingEventArgs e)
{
if (cdDataSet.HasChanges()) {
switch (MessageBox.Show("The data has been changed. Press:\n" +
"Yes - to save data to the file\n" +
"No - to discard changes\n" +
"Cancel - to cancel closing the application",
"THE DATA HAS BEEN CHANGED",
MessageBoxButtons.YesNoCancel))
{
case DialogResult.Yes: // save data to the file
try {
tblAuthorsTableAdapter.Update(cdDataSet.tblAuthors);
}
catch (Exception exc) {
MessageBox.Show("EXCEPTION: " + exc.ToString());
}
break;
case DialogResult.No: // discard changes
break;
case DialogResult.Cancel: // cancel closing the application
e.Cancel = true;
break;
}
}
}
- Creating SQL Server database programmatically.
- Use the following code to create a database in SQL Server 2005 Express
programmatically.
SqlConnection myConn = new SqlConnection(
"Server=MOSS\\SQLEXPRESS;Integrated security=SSPI;database=master");
try {
myConn.Open();
string str = "CREATE DATABASE mySecondDatabase";
SqlCommand myCommand = new SqlCommand(str, myConn);
myCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
MessageBox.Show("DataBase is Created Successfully");
}
catch (System.Exception ex) {
MessageBox.Show(ex.ToString());
}
finally {
if (myConn.State == ConnectionState.Open) {
myConn.Close();
}
}
- Make sure to change the connection string, in particular the name of the SQL
Server instance
- If you want to create your database in non-standard location or to specify
some advanced properties, you can define more details in CREATE DATABASE command:
str = "CREATE DATABASE MyDatabase ON PRIMARY " +
"(NAME = MyDatabase_Data, " +
"FILENAME = 'C:\\MyDatabaseData.mdf', " +
"SIZE = 2MB, MAXSIZE = 10MB, FILEGROWTH = 10%) " +
"LOG ON (NAME = MyDatabase_Log, " +
"FILENAME = 'C:\\MyDatabaseLog.ldf', " +
"SIZE = 1MB, " +
"MAXSIZE = 5MB, " +
"FILEGROWTH = 10%)";
- Create tables in your new database using CREATE TABLE commands.
SqlConnection myConn = new SqlConnection(
"Server=MOSS\\SQLEXPRESS;Integrated security=SSPI;database=mySecondDatabase");
try {
myConn.Open();
string str = "CREATE TABLE tblAuthors (" +
"ID int PRIMARY KEY, " +
"Name varchar(100))";
SqlCommand myCommand = new SqlCommand(str, myConn);
myCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
str = "CREATE TABLE tblRecords (" +
"ID int PRIMARY KEY, " +
"IDAuthor int FOREIGN KEY REFERENCES tblAuthors (ID), " +
"Name varchar(100))";
myCommand.CommandText = str;
myCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
MessageBox.Show("Tables in the Database are Created Successfully");
}
catch (System.Exception ex) {
MessageBox.Show(ex.ToString());
}
finally {
if (myConn.State == ConnectionState.Open) {
myConn.Close();
}
}
- Note the name of a database used in a connection string.
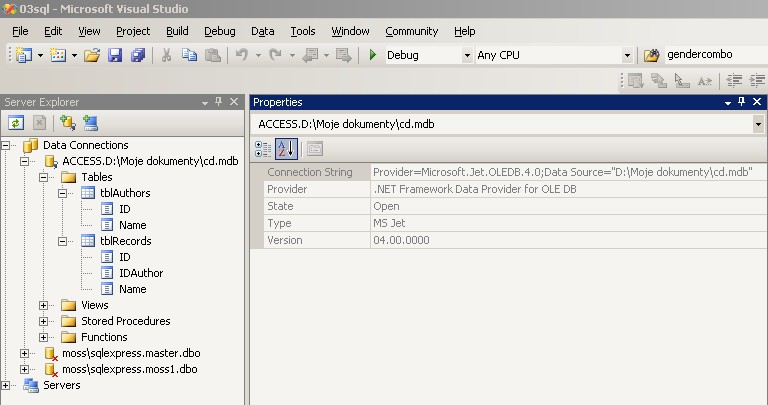
- Write a code to load all data from cd.mdb Access file.
- The simplest way to find correct connection string to any database is to use
Visual Studio's Server Explorer
- Use the following code to copy all data from Access to SQL Server database.
OleDbConnection accConn = new OleDbConnection(
"Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source=\"D:\\Moje dokumenty\\cd.mdb\"");
SqlConnection sqlConn = new SqlConnection(
"Server=MOSS\\SQLEXPRESS;Integrated security=SSPI;database=mySecondDatabase");
try {
accConn.Open();
sqlConn.Open();
// Authors
string str = "SELECT ID, Name FROM tblAuthors";
OleDbCommand accCommand = new OleDbCommand(str, accConn);
OleDbDataReader reader = accCommand.ExecuteReader();
if (reader.HasRows) {
while (reader.Read()) {
int id = reader.GetInt32(0);
string name = reader.GetString(1);
name = name.Replace("\'", "\'\'");
str = "INSERT INTO tblAuthors (ID, Name) " +
"VALUES (" + id + ", \'" + name + "\')";
SqlCommand sqlCommand = new SqlCommand(str, sqlConn);
sqlCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
reader.Dispose();
// Records
str = "SELECT ID, IDAuthor, Name FROM tblRecords";
accCommand.CommandText = str;
reader = accCommand.ExecuteReader();
if (reader.HasRows) {
while (reader.Read()) {
int id = reader.GetInt32(0);
int idAuthor = reader.GetInt32(1);
string name = reader.GetString(2);
name = name.Replace("\'", "\'\'");
str = "INSERT INTO tblRecords (ID, IDAuthor, Name) " +
"VALUES (" + id + ", " + idAuthor + ", \'" + name + "\')";
SqlCommand sqlCommand = new SqlCommand(str, sqlConn);
sqlCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
}
reader.Dispose();
MessageBox.Show("The data has been copied successfully");
}
catch (Exception ex) {
MessageBox.Show(ex.ToString());
}
finally {
if (accConn.State == ConnectionState.Open) {
accConn.Close();
}
if (sqlConn.State == ConnectionState.Open) {
sqlConn.Close();
}
}
- Notice the order of adding data to SQL Server's database: records after
authors. Such order is necessary due to contraints declared in tables
(foreign key in tblRecords table).
- Notice also duplicating apostrophes in strings added to SQL Server tables.
- Now we have two databases with the same structure, so we can demonstrate new feature
of ADO.NET 2.0 - database independent operations using DbProviderFactory.
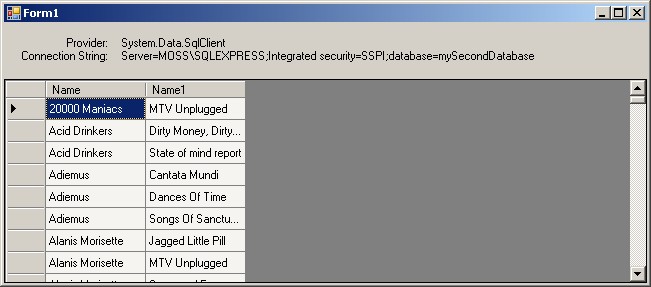
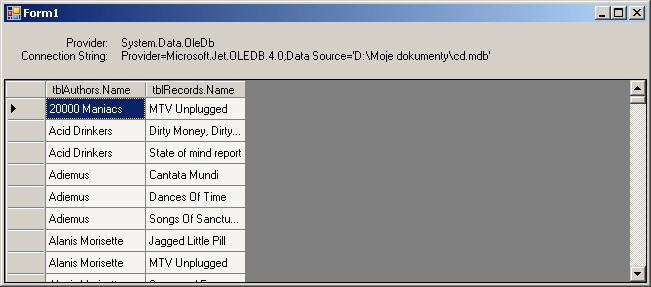
- Add the following code to a handler of Load event:
IDataReader dbreader = null;
ConnectionStringSettings settings = ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings["myConnectionString"];
providerLabel.Text = settings.ProviderName;
connectionStringLabel.Text = settings.ConnectionString;
DbProviderFactory dbfactory = DbProviderFactories.GetFactory(settings.ProviderName);
IDbConnection dbconn = dbfactory.CreateConnection();
dbconn.ConnectionString = settings.ConnectionString;
try {
dbconn.Open();
IDbCommand dbcomm = dbconn.CreateCommand();
dbcomm.Connection = dbconn;
dbcomm.CommandText = "SELECT tblAuthors.Name, tblRecords.Name " +
"FROM tblAuthors, tblRecords " +
"WHERE tblAuthors.ID = tblRecords.IDAuthor " +
"ORDER BY tblAuthors.Name, tblRecords.Name";
dbreader = dbcomm.ExecuteReader(CommandBehavior.CloseConnection);
DataSet ds = new DataSet();
ds.Load(dbreader, LoadOption.PreserveChanges, new string[] { "All" });
dataGridView1.DataSource = ds.Tables[0];
}
catch(Exception ex) {
MessageBox.Show("EXCEPTION: " + ex.ToString());
}
finally {
if(dbreader != null) {
dbreader.Dispose();
}
if(dbconn.State == ConnectionState.Open) {
dbconn.Close();
}
}
 Replace a content of the configuration file with the following:
Replace a content of the configuration file with the following:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<configuration>
<connectionStrings>
<add name="myConnectionString"
connectionString="Provider=Microsoft.Jet.OLEDB.4.0;Data Source='D:\Moje dokumenty\cd.mdb';"
providerName="System.Data.OleDb" />
</connectionStrings>
</configuration>
Run the application without any changes in the source code - it works now with
data read from Access file.
 Investigate machine.config file
(C:\WINDOWS\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v2.0.50727\CONFIG\machine.config) and find
DbProviderFactories section to understand the way DbProviderFactory works.
Investigate machine.config file
(C:\WINDOWS\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v2.0.50727\CONFIG\machine.config) and find
DbProviderFactories section to understand the way DbProviderFactory works.