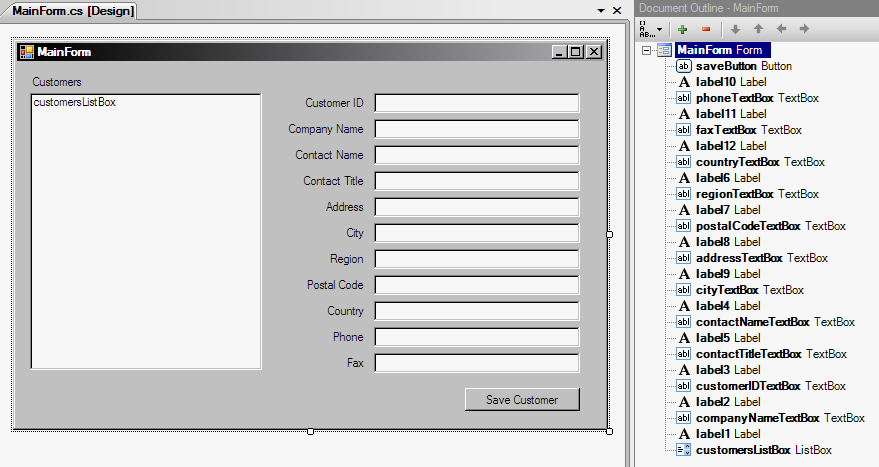
- Add an "Application Configuration File" to the project (the App.config item will appear in the Solution Explorer window).
- Add the connectionStrings section with configuration of the connection string,
e.g.:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>(In the above example connection is configured for the SQL Server instance with name KMOSSAKOWSKI\SQLEXPRESS, the name of the database is Northwind, the SQL Server authentication is used with login: nu and password: nu. Be sure to modify the connection string to work properly with your SQL Server instance.)
<configuration>
<connectionStrings>
<add name="NorthwindDb"
connectionString="server=KMOSSAKOWSKI\SQLEXPRESS; uid=nu; pwd=nu; initial catalog=Northwind"
providerName="System.Data.SqlClient" />
</connectionStrings>
</configuration>
- Add a reference to the System.Configuration assembly.
- In the constructor write code loading the connection string from the
configuration file:class DBManager
{
private DbConnection connection;
private DbProviderFactory factory;
public DBManager()
{
ConnectionStringSettings css =
ConfigurationManager.ConnectionStrings["NorthwindDb"];
factory = DbProviderFactories.GetFactory(css.ProviderName);
connection = factory.CreateConnection();
connection.ConnectionString = css.ConnectionString;
}
public void OpenConnection()
{
connection.Open();
}
public void CloseConnection()
{
if (connection.State == ConnectionState.Open)
{
connection.Close();
}
}
}- If it is possible, it is a good idea to write database management code independent on the database engine. Such solution allows to use the same code in many projects.
private
DBManager
dbManager;
protected override void OnLoad(EventArgs e)
{
base.OnLoad(e);
try
{
dbManager = new DBManager();
dbManager.OpenConnection();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message, "Exception at opening the database connection");
Close();
}
}
protected override
void OnClosed(EventArgs
e)
{
base.OnClosed(e);
try
{
dbManager.CloseConnection();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message, "Exception at closing the database connection");
}
}
{
base.OnClosed(e);
try
{
dbManager.CloseConnection();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message, "Exception at closing the database connection");
}
}
class
Customer
{
public string CustomerID { get; set; }
public string CompanyName { get; set; }
public string ContactName { get; set; }
public string ContactTitle { get; set; }
public string Address { get; set; }
public string City { get; set; }
public string Region { get; set; }
public string PostalCode { get; set; }
public string Country { get; set; }
public string Phone { get; set; }
public string Fax { get; set; }
public Customer(string customerID, string companyName)
{
CustomerID = customerID;
CompanyName = companyName;
}
}
{
public string CustomerID { get; set; }
public string CompanyName { get; set; }
public string ContactName { get; set; }
public string ContactTitle { get; set; }
public string Address { get; set; }
public string City { get; set; }
public string Region { get; set; }
public string PostalCode { get; set; }
public string Country { get; set; }
public string Phone { get; set; }
public string Fax { get; set; }
public Customer(string customerID, string companyName)
{
CustomerID = customerID;
CompanyName = companyName;
}
}
public
DbDataReader
ExecuteReader(string sqlQuery)
{
DbCommand cmd = connection.CreateCommand();
cmd.CommandText = sqlQuery;
return cmd.ExecuteReader();
}
{
DbCommand cmd = connection.CreateCommand();
cmd.CommandText = sqlQuery;
return cmd.ExecuteReader();
}
class
CustomersList :
List<Customer>
{
public void Load(DBManager dbManager)
{
DbDataReader reader = dbManager.ExecuteReader(
@"SELECT
CustomerID,
CompanyName
FROM
Customers");
if (reader.HasRows)
{
while (reader.Read())
{
Customer customer = new Customer(reader.GetString(0), reader.GetString(1));
Add(customer);
}
}
reader.Close();
}
}
{
public void Load(DBManager dbManager)
{
DbDataReader reader = dbManager.ExecuteReader(
@"SELECT
CustomerID,
CompanyName
FROM
Customers");
if (reader.HasRows)
{
while (reader.Read())
{
Customer customer = new Customer(reader.GetString(0), reader.GetString(1));
Add(customer);
}
}
reader.Close();
}
}
private
void
FillCustomersList()
{
CustomersList customersList = new CustomersList();
customersList.Load(dbManager);
customersListBox.DisplayMember = "CompanyName";
customersListBox.ValueMember = "CustomerID";
customersListBox.DataSource = customersList;
}
{
CustomersList customersList = new CustomersList();
customersList.Load(dbManager);
customersListBox.DisplayMember = "CompanyName";
customersListBox.ValueMember = "CustomerID";
customersListBox.DataSource = customersList;
}
- The DisplayMember, ValueMember, and DataSource properties allow to bind data to the ListBox. Using these methods allows to minimize the code for adding items to the list.
private
bool wasLoaded =
false;
public void Load(DBManager dbManager)
{
if (!wasLoaded)
{
DbDataReader reader = dbManager.ExecuteReader(string.Format(
@"SELECT
CompanyName,
ContactName,
ContactTitle,
Address,
City,
Region,
PostalCode,
Country,
Phone,
Fax
FROM
Customers
WHERE
CustomerID = '{0}'",
CustomerID));
if (reader.HasRows && reader.Read())
{
CompanyName = reader.GetString(0);
ContactName = reader.GetString(1);
ContactTitle = reader.GetValue(2) as string;
Address = reader.GetValue(3) as string;
City = reader.GetValue(4) as string;
Region = reader.GetValue(5) as string;
PostalCode = reader.GetValue(6) as string;
Country = reader.GetValue(7) as string;
Phone = reader.GetValue(8) as string;
Fax = reader.GetValue(9) as string;
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("Customer not found.");
}
reader.Close();
wasLoaded = true;
}
}
public void Load(DBManager dbManager)
{
if (!wasLoaded)
{
DbDataReader reader = dbManager.ExecuteReader(string.Format(
@"SELECT
CompanyName,
ContactName,
ContactTitle,
Address,
City,
Region,
PostalCode,
Country,
Phone,
Fax
FROM
Customers
WHERE
CustomerID = '{0}'",
CustomerID));
if (reader.HasRows && reader.Read())
{
CompanyName = reader.GetString(0);
ContactName = reader.GetString(1);
ContactTitle = reader.GetValue(2) as string;
Address = reader.GetValue(3) as string;
City = reader.GetValue(4) as string;
Region = reader.GetValue(5) as string;
PostalCode = reader.GetValue(6) as string;
Country = reader.GetValue(7) as string;
Phone = reader.GetValue(8) as string;
Fax = reader.GetValue(9) as string;
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("Customer not found.");
}
reader.Close();
wasLoaded = true;
}
}
- The wasLoaded flag is used to prevent reloading data of the customer (according to one of assumption, only once instance of this appplication is run and this is the only client for the database).
- Using the DbDataReader.GetValue method instead of GetString allows to handle in an easy way null values in the database.
private
void
FillCustomerFields(Customer customer)
{
customerIDTextBox.Text = customer.CustomerID;
companyNameTextBox.Text = customer.CompanyName;
contactNameTextBox.Text = customer.ContactName;
contactTitleTextBox.Text = customer.ContactTitle;
addressTextBox.Text = customer.Address;
cityTextBox.Text = customer.City;
regionTextBox.Text = customer.Region;
postalCodeTextBox.Text = customer.PostalCode;
countryTextBox.Text = customer.Country;
phoneTextBox.Text = customer.Phone;
faxTextBox.Text = customer.Fax;
saveButton.Enabled = true;
}
private void customersListBox_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (customersListBox.SelectedItem != null)
{
Customer customer = customersListBox.SelectedItem as Customer;
try
{
customer.Load(dbManager);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message, "Exception at loading customer's data");
}
FillCustomerFields(customer);
}
}
{
customerIDTextBox.Text = customer.CustomerID;
companyNameTextBox.Text = customer.CompanyName;
contactNameTextBox.Text = customer.ContactName;
contactTitleTextBox.Text = customer.ContactTitle;
addressTextBox.Text = customer.Address;
cityTextBox.Text = customer.City;
regionTextBox.Text = customer.Region;
postalCodeTextBox.Text = customer.PostalCode;
countryTextBox.Text = customer.Country;
phoneTextBox.Text = customer.Phone;
faxTextBox.Text = customer.Fax;
saveButton.Enabled = true;
}
private void customersListBox_SelectedIndexChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (customersListBox.SelectedItem != null)
{
Customer customer = customersListBox.SelectedItem as Customer;
try
{
customer.Load(dbManager);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message, "Exception at loading customer's data");
}
FillCustomerFields(customer);
}
}
- The SelectedItem property of the ListBox can be cast to the Customer class because the DataSource property of the ListBox was set to a list of Customer objects.
public
int ExecuteNonQuery(DbCommand cmd)
{
return cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
public DbCommand CreateCommand(string sql)
{
DbCommand cmd = connection.CreateCommand();
cmd.CommandText = sql;
return cmd;
}
public void AddInputParameter(DbCommand cmd, string name, object value)
{
DbParameter parameter = factory.CreateParameter();
parameter.Direction = ParameterDirection.Input;
parameter.ParameterName = name;
parameter.Value = value ?? DBNull.Value;
cmd.Parameters.Add(parameter);
}
{
return cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
}
public DbCommand CreateCommand(string sql)
{
DbCommand cmd = connection.CreateCommand();
cmd.CommandText = sql;
return cmd;
}
public void AddInputParameter(DbCommand cmd, string name, object value)
{
DbParameter parameter = factory.CreateParameter();
parameter.Direction = ParameterDirection.Input;
parameter.ParameterName = name;
parameter.Value = value ?? DBNull.Value;
cmd.Parameters.Add(parameter);
}
- Note the way of setting the value of a parameter - the special value DBNull.Value is used instead of the null value. Trying to execute command with the null value would throw an exception with a message that an expected parameter was not provided.
public
void Save(DBManager dbManager)
{
DbCommand cmd = dbManager.CreateCommand(string.Format(
@"UPDATE
Customers
SET
CompanyName = @CompanyName,
ContactName = @ContactName,
ContactTitle = @ContactTitle,
Address = @Address,
City = @City,
Region = @Region,
PostalCode = @PostalCode,
Country = @Country,
Phone = @Phone,
Fax = @Fax
WHERE
CustomerID = '{0}'",
CustomerID));
dbManager.AddInputParameter(cmd, "CompanyName", CompanyName);
dbManager.AddInputParameter(cmd, "ContactName", ContactName);
dbManager.AddInputParameter(cmd, "ContactTitle", ContactTitle);
dbManager.AddInputParameter(cmd, "Address", Address);
dbManager.AddInputParameter(cmd, "City", City);
dbManager.AddInputParameter(cmd, "Region", Region);
dbManager.AddInputParameter(cmd, "PostalCode", PostalCode);
dbManager.AddInputParameter(cmd, "Country", Country);
dbManager.AddInputParameter(cmd, "Phone", Phone);
dbManager.AddInputParameter(cmd, "Fax", Fax);
if (dbManager.ExecuteNonQuery(cmd) != 1)
{
MessageBox.Show("Error saving data - 0 or more than 1 row updated");
}
}
{
DbCommand cmd = dbManager.CreateCommand(string.Format(
@"UPDATE
Customers
SET
CompanyName = @CompanyName,
ContactName = @ContactName,
ContactTitle = @ContactTitle,
Address = @Address,
City = @City,
Region = @Region,
PostalCode = @PostalCode,
Country = @Country,
Phone = @Phone,
Fax = @Fax
WHERE
CustomerID = '{0}'",
CustomerID));
dbManager.AddInputParameter(cmd, "CompanyName", CompanyName);
dbManager.AddInputParameter(cmd, "ContactName", ContactName);
dbManager.AddInputParameter(cmd, "ContactTitle", ContactTitle);
dbManager.AddInputParameter(cmd, "Address", Address);
dbManager.AddInputParameter(cmd, "City", City);
dbManager.AddInputParameter(cmd, "Region", Region);
dbManager.AddInputParameter(cmd, "PostalCode", PostalCode);
dbManager.AddInputParameter(cmd, "Country", Country);
dbManager.AddInputParameter(cmd, "Phone", Phone);
dbManager.AddInputParameter(cmd, "Fax", Fax);
if (dbManager.ExecuteNonQuery(cmd) != 1)
{
MessageBox.Show("Error saving data - 0 or more than 1 row updated");
}
}
private
void
SetCustomerFromFields(Customer customer)
{
customer.CustomerID = customerIDTextBox.Text;
customer.CompanyName = companyNameTextBox.Text;
customer.ContactName = contactNameTextBox.Text;
customer.ContactTitle = contactTitleTextBox.Text;
customer.Address = addressTextBox.Text;
customer.City = cityTextBox.Text;
customer.Region = regionTextBox.Text;
customer.PostalCode = postalCodeTextBox.Text;
customer.Country = countryTextBox.Text;
customer.Phone = phoneTextBox.Text;
customer.Fax = faxTextBox.Text;
}
private void saveButton_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (customersListBox.SelectedItem != null)
{
Customer customer = customersListBox.SelectedItem as Customer;
SetCustomerFromFields(customer);
try
{
customer.Save(dbManager);
MessageBox.Show("Customer saved.");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message, "Exception at saving customer's data");
}
}
}
{
customer.CustomerID = customerIDTextBox.Text;
customer.CompanyName = companyNameTextBox.Text;
customer.ContactName = contactNameTextBox.Text;
customer.ContactTitle = contactTitleTextBox.Text;
customer.Address = addressTextBox.Text;
customer.City = cityTextBox.Text;
customer.Region = regionTextBox.Text;
customer.PostalCode = postalCodeTextBox.Text;
customer.Country = countryTextBox.Text;
customer.Phone = phoneTextBox.Text;
customer.Fax = faxTextBox.Text;
}
private void saveButton_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (customersListBox.SelectedItem != null)
{
Customer customer = customersListBox.SelectedItem as Customer;
SetCustomerFromFields(customer);
try
{
customer.Save(dbManager);
MessageBox.Show("Customer saved.");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.Message, "Exception at saving customer's data");
}
}
}